Animal Phylogenetic Tree
Treefam is a database of phylogenetic trees of gene families found in animals. Phylogenetic trees are depicted somewhat differently.
Solved What does the tree (see Fig. 28.4
• internal nodes are generally called hypothetical taxonomic units • in a phylogenetic tree, each node with

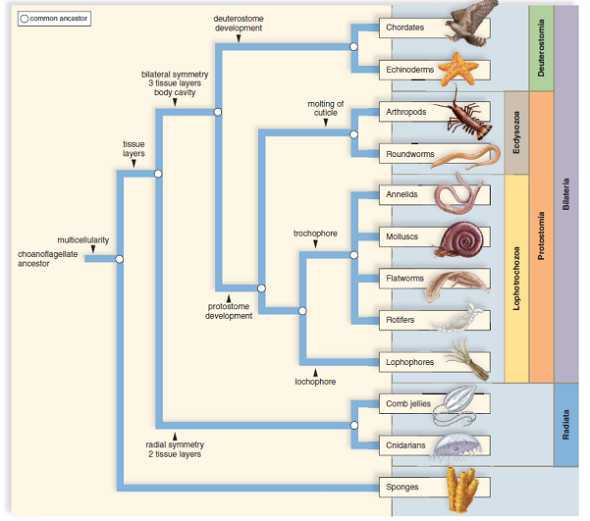
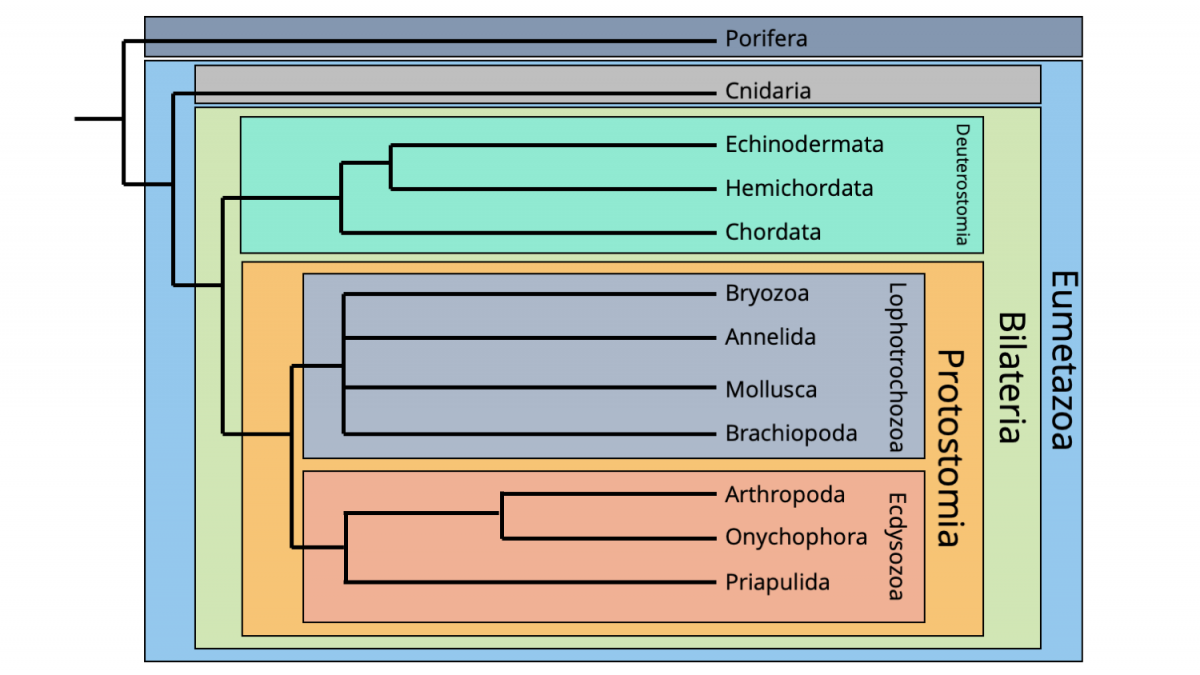
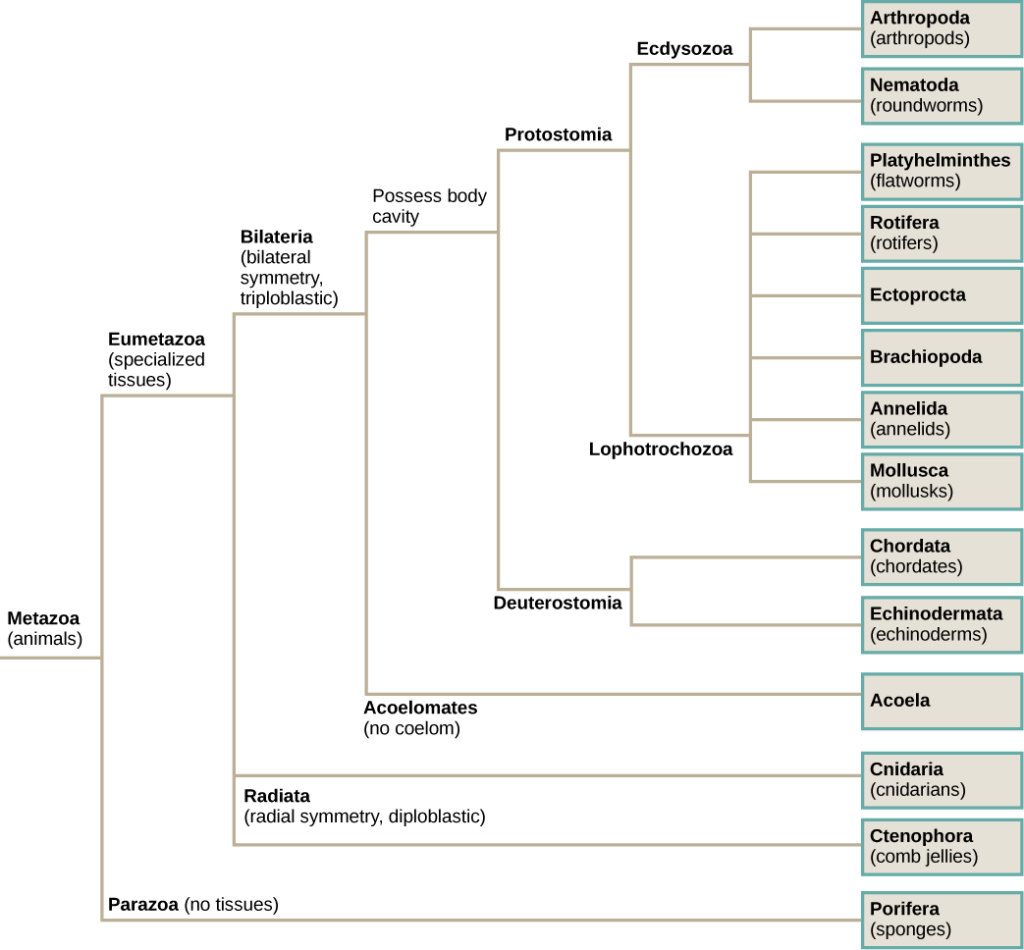
Animal phylogenetic tree. The current understanding of evolutionary relationships between animal, or metazoa, phyla begins with the distinction between “true” animals with true differentiated tissues, called eumetazoa, and animal phyla that do not have true differentiated tissues (such as the sponges), called parazoa.both parazoa and eumetazoa. A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents. Constructing an animal phylogenetic tree.
The current understanding of evolutionary relationships between animal, or metazoa, phyla begins with the distinction between “true” animals with true differentiated tissues, called eumetazoa, and animal phyla that do not have true differentiated tissues (such as the sponges), called parazoa. Phylogenetic (evolutionary) tree • showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities that are believed to have a common ancestor. Constructing an animal phylogenetic tree.
What is a phylogenetic tree of animals? And animal pathogenicity by ascomycetous fungi. Thus, these characteristics differentiate between the animals mentioned in the diagram that nevertheless have the same.
Fox animal phylogenetic tree diagrams showcase different evolution stages of a fox starting from canis lupus familiaris, canis lupus, canis latrans, canis rufus, vulpes zerda, vulpes lagopus, vulpes, lycaon pictus, and more. The study of phylogeny (the branching sequence of evolution) aims to determine the evolutionary relationships between phyla. In particular, they clarify whether certain traits are homologous (found in the.
Curated families are being added progressively, base. Phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree) is a diagram or tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. In the first section, the phylogenetic relationships in the ascomycota with a tree inferred from 297 18s rrna gene sequences from genbank are summarized.
With the metazoan phylogenetic tree, you can illustrate different animals from the kingdom, like porifera, ctenophora, cnidaria, acoela, echinodermata, chordata, mollusca, annelida, brachiopoda, ectoprocta, rotifera, platyhelminthes, nematoda, and arthropoda. The review is divided into four sections. The gene page provides a list of the animal and yeast/plant orthologs of that gene that were inferred from the phylogenetic tree for the full family.
Today’s views of the animal tree of life are the result of decades of intense phylogenetic research, in terms of both data—first anatomical and Major features of animal phylogeny. A support value is given for each pair of orthologs, which is the frequency at which that particular orthology assignment was observed among a set of 100 bootstrap trees ( 39 , 40 ).
Understanding phylogenetic trees phylogeny = the pattern of evolutionary relationships among species, their descent from common ancestors what is phylogeny? As new animal phylogeny (adoutte et. 1999, 2000, 2003) the result soon entered the textbooks of zoology.
(2015).importantly, the phylogenetic tree below omits numerous animal phyla that left behind little or no fossil record. Imagine that you are holding the family tree for the big cats shown in fig. A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a diagrammatic representation of the evolutionary relationships among various taxa.
The tree of life shows how all life on earth is related. The current understanding of evolutionary relationships among animal, or metazoa, phyla begins with the distinction between animals with true differentiated tissues, called eumetazoa, and animal phyla that do not have true differentiated tissues, such as the sponges (porifera) and the placozoa.similarities between. A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics.
It aims to develop a curated resource that presents the accurate evolutionary history of all animal gene families, as well as reliable ortholog and paralog assignments. Each leaf represents a different species. Constructing an animal phylogenetic tree.
Constructing an animal phylogenetic tree. The current understanding of evolutionary relationships among animal, or metazoa, phyla begins with the distinction between animals with true differentiated tissues, called eumetazoa, and animal phyla that do not have true differentiated tissues, such as the sponges (porifera) and the placozoa.similarities between the feeding cells. These characteristics are jaws, lungs, gizzards, and feathers.
The current understanding of evolutionary relationships between animal, or metazoa, phyla begins with the distinction between “true” animals with true differentiated tissues, called eumetazoa, and animal phyla that do not have true differentiated tissues (such as the sponges), called parazoa.both parazoa and eumetazoa. Since the publication of haeckel’s (1866) animal tree of life, zoologists have made great progress in understanding animal evolutionary relationships. The new animal phylogeny overturned the traditional phylogenetic trees that had been established by the old method of comparative morphology.
Currently, most biologists divide the animal kingdom into 35 to 40 phyla. Scientists develop phylogenetic trees, which serve as hypotheses about which species have evolved from which ancestors. Using the gene tree, it was explored whether gains and losses of plant and animal
In our interactive tree of life you can explore the relationships between 2,235,322 species and wonder at 105,319 images on a single zoomable page. Constructing an animal phylogenetic tree. Constructing an animal phylogenetic tree.
Now, flip it sideways (rotate 90° counterclockwise) and you have the image shown in 2b. • each node is called a taxonomic unit. Evolutionary trees, or phylogeny, is the formal study of organisms and their evolutionary history with respect to each other.
Family trees tend to be drawn as if they were hanging upside down, like a cluster of grapes. Animal phylogenetic tree as you can see in the diagram, all animals have the same common ancestor, but they are divided because of their different characteristics. The branches show how these many species evolved from common ancestors over billions of years.
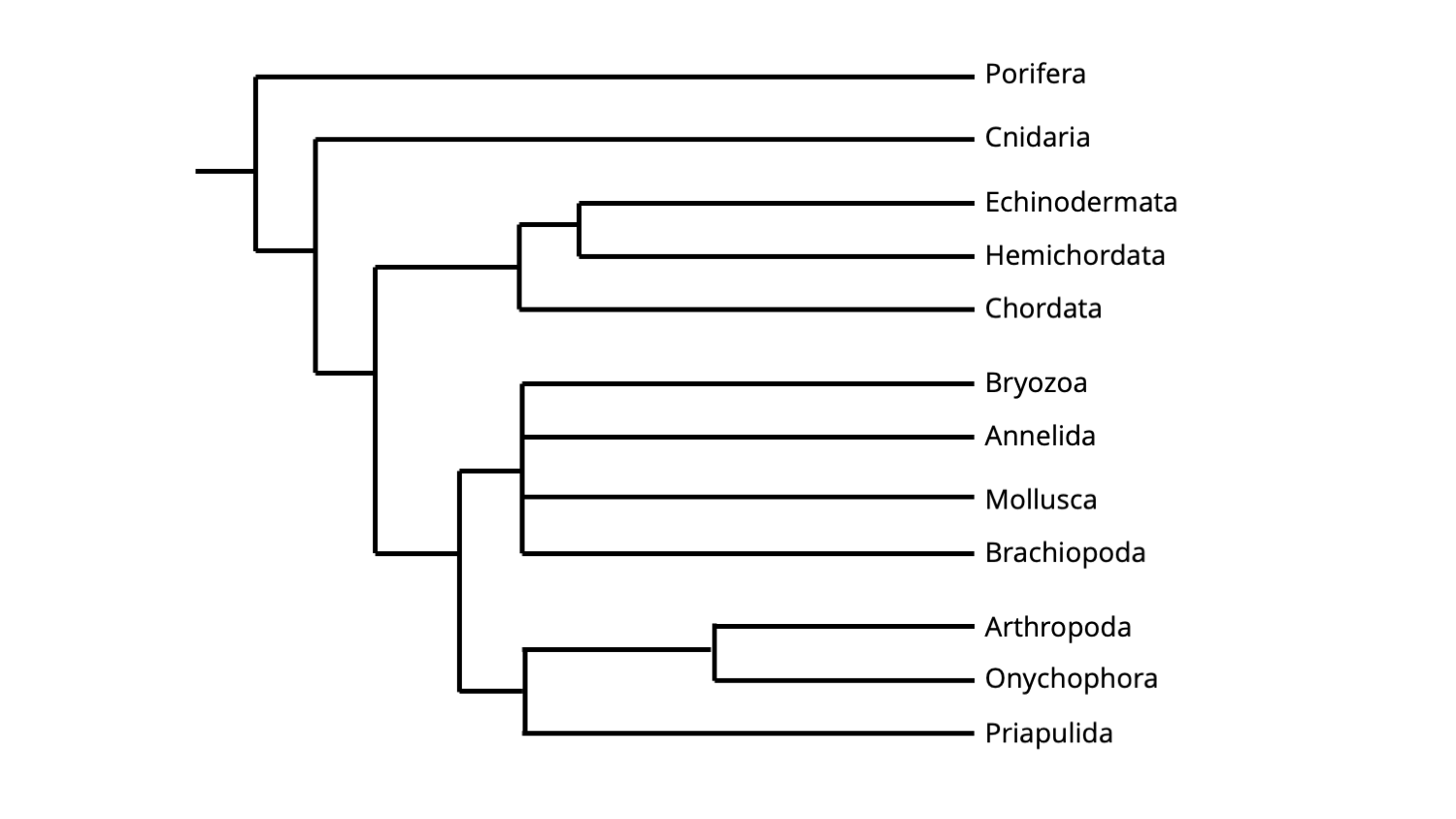
The phylogenetic framework followed here is derived and highly simplified from the molecular phylogenetic hypothesis recently presented by telford et al.
Animals Vertebrates Organismal Biology
Animal Phylogeny Digital Atlas of Ancient Life

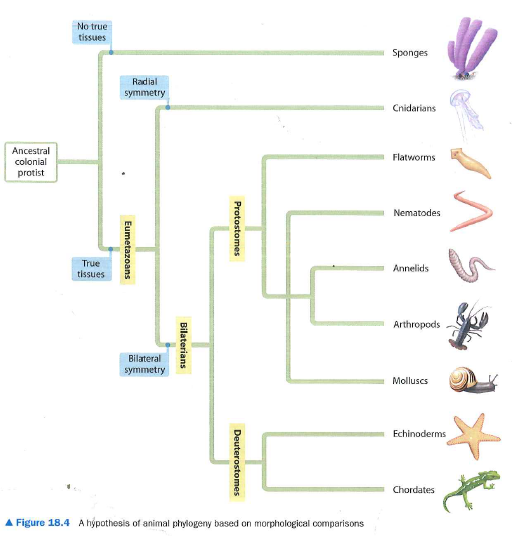
Figure 19.1. The animal family tree The traditional
Phylogenomic Insights into Animal Evolution Current Biology
tree traits. Animal Phylogeny. 20190907
A simplified tree of animals showing the
Parasite, Jellyfish Related Environment News

36 best images about Animaphyl on Pinterest Life cycles
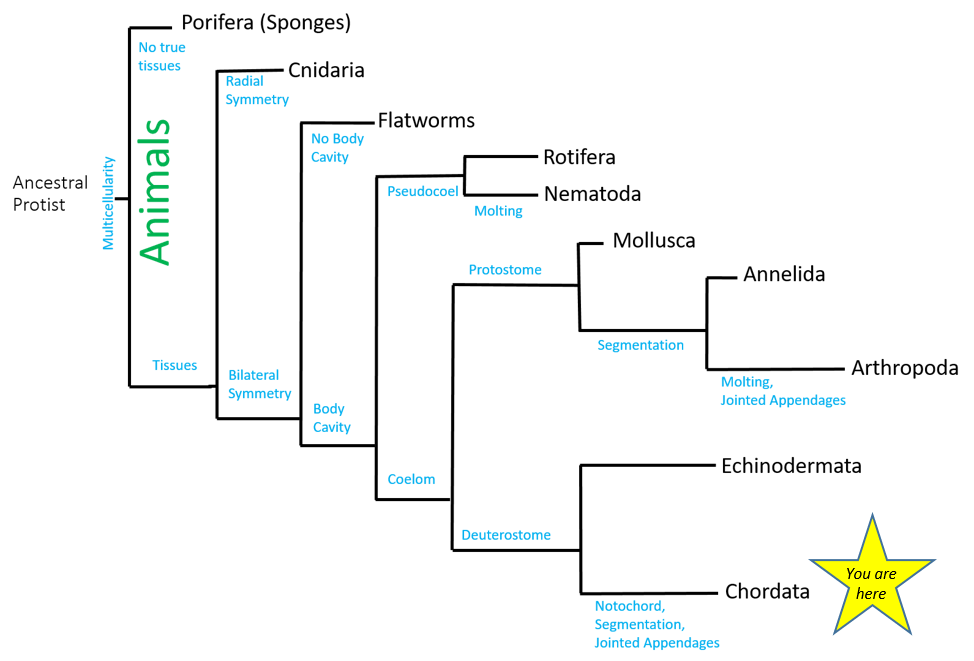
Solved Compare the tree from Module 18.4
PPT The Animal Kingdom! PowerPoint Presentation ID2621750
Animals Invertebrates Biology 1520

A simplified tree of multicellular animals

Kingdom Animalia includes phylums tree
Animal Phylogeny Digital Atlas of Ancient Life

Post a Comment for "Animal Phylogenetic Tree"