Pneumonia In Animals
Coughing and dyspnea are the most common clinical signs, which can be exacerbated by concomitant bacterial or viral infections. Canine distemper virus, adenovirus types 1 and 2, parainfluenza virus, and feline.
Vaccination against pneumonia represents real value for
The union of international associations (uia) is a research institute and documentation centre, based in brussels.
Pneumonia in animals. The important bacteria are pasteurella haemolytica (now known as mannheimia haemolytica), pasteurella multocida, histophilus somni and mycoplasma bovis. (ii) defining pneumonia as a group of specific. It is not a very common disorder among ordinary pets, but it can be very serious for those who get it.
There are different types of pneumonia depending on the cause, which can be divided into three categories: A short, productive cough and/or a thick, mucoid to mucopurulent nasal discharge may be present. The most common material aspirated in large animals is a large volume of liquid, due to weakness from a different primary problem or iatrogenically during oral administration of fluids or other treatments.
Diseases of respiratory system pneumonia in dogs ad cats prof. Pneumonia is a major cause of death and economic losses to the cattle industry. Pneumonia is commonly classified by its original cause:
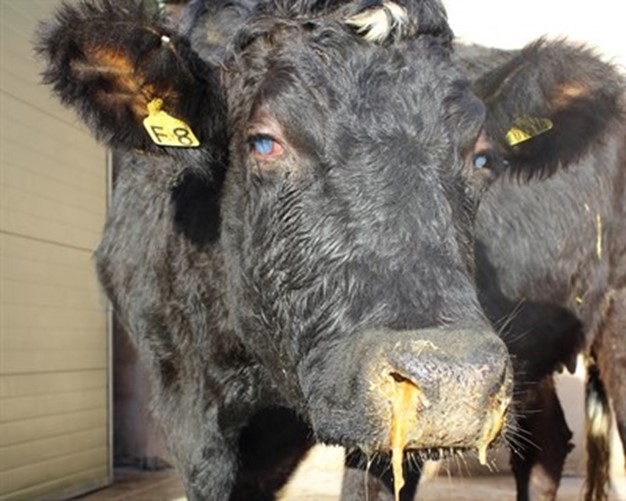
How does a cow get pneumonia? Pneumonia results in an inability to oxygenate the blood, leading to lethargy and shortness of breath. The most common course of disease is chronic.
Bacterial pneumonias consist of br. It was established in 1907, by henri la fontaine (nobel peace prize laureate of 1913), and paul otlet, a founding father of what is now called information science. Viral pneumonia (usually the result of canine distemper virus infection, canine influenza virus, or a complicated feline upper respiratory infection).
Animals with pneumonia can have hyperemia of the epithelium, prominent mucosal vessels, and evidence of airway inflammation, appearing as rounded, thickened airway bifurcations and airway nodules. Inflammation of the lung tissue that usually preceded by bronchitis (bronchopneumonia) it is characterized clinically by. Fungal pneumonia (caused by a fungus, typically coccidioidomycosis immitis, cryptococcus neoformans or other fungi).
Environmental factors are also extremely crucial in managing the disease. At this point, it’s especially relevant to mention pneumonia by aspiration. Pneumonia is more common in the dog than the cat, and the most common causes of pneumonia are infectious in origin.
It is the most common cause of death in cattle of all ages over one month old. Inflammation also stimulates excessive secretion of airway fluid and mucus, resulting in cough and difficulty breathing. Lungworm infection, also known as verminous bronchitis or verminous pneumonia, is an inflammatory disease of the lower respiratory tract caused by a variety of nematodes.
Recognizing the patterns of pneumonic lesions and understanding the pathogenesis of the various types of pneumonia are important for correct diagnosis and interpretation of the lesions. Pets suffering from pneumonia will breathe quickly, cough, maybe have a fever and generally act lethargic. This occurs frequently as a result of the aspiration of vomit and regurgitation in animals that have fainted.
The usual cause is primary viral infection of the lower respiratory tract. In order to help prevent the spread of the virus or bacteria, our vets recommend keeping your sick cat separated from other pets in your household. Pneumonia in pet animals 1.
The different types of pneumonia in animals. In order to prevent this complication, it’s vitally important to position animals with their back third slightly elevated. Clinical clinical findings were similar to the one developed in humans, and include cough, tachypnea, dyspnea,
The commentary then calls for debate to generate consensus classifications in the field, proposing a working definition and way forward focusing on the following three points: Fungal pneumonia is more commonly seen in small animals than in large. The baermann technique is used to detect first.
Dairy calves are likely to suffer from the disease at any age, with it manifesting itself as a chronic, coughing pneumonia, or as a more acute, enzootic calf pneumonia. Viral or bacterial pneumonia is contagious and can easily be passed along to other cats, dogs, and small animals. Aspiration pneumonia is a lung disease characterized by inflammation and necrosis due to inhalation of foreign material.
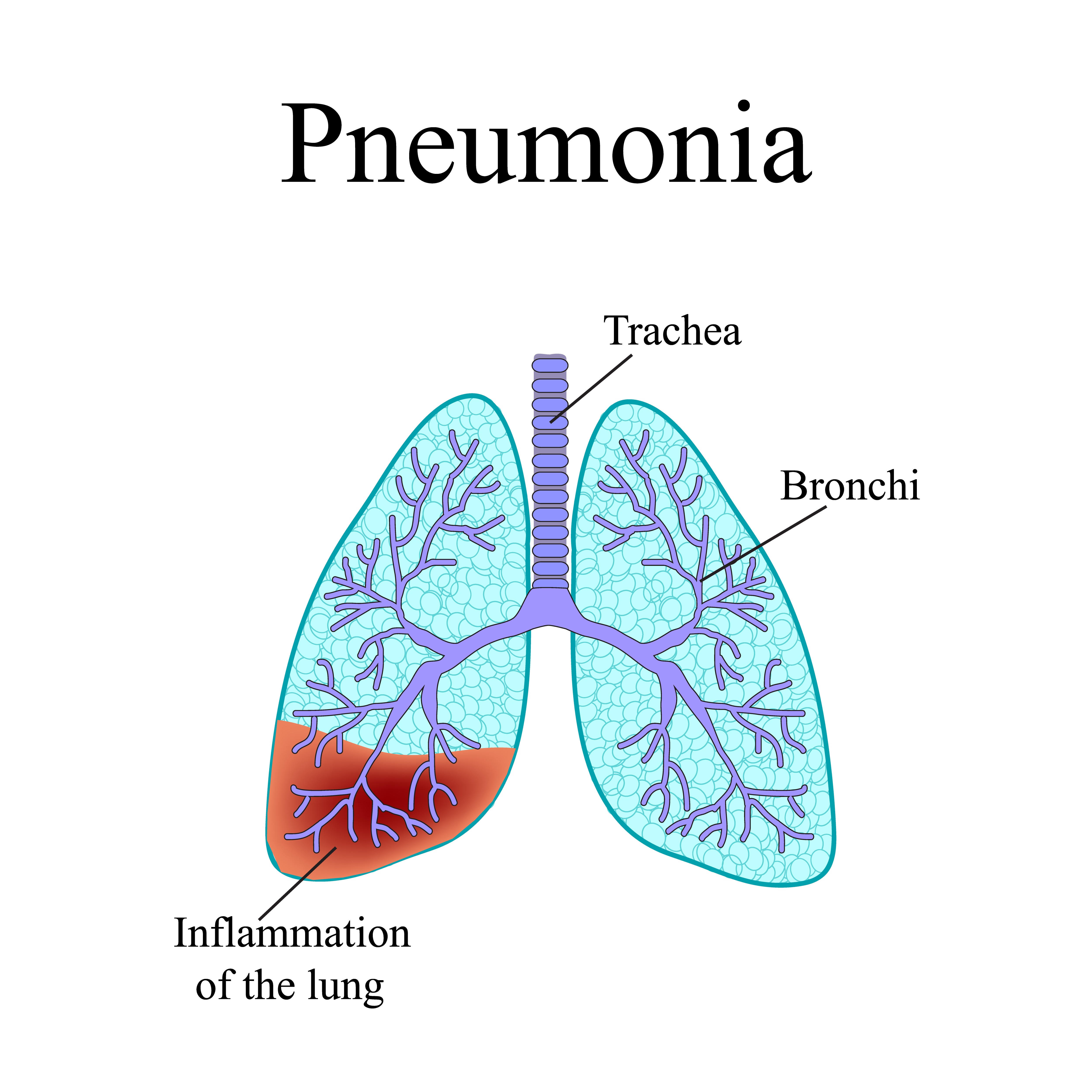
Pneumonia is an acute or chronic inflammation of the lungs and bronchi characterized by disturbance in respiration and hypoxemia and complicated by the systemic effects of associated toxins. Pneumonia is a condition which refers to an inflammation of the lungs. Human pneumonia is modeled with experimental infections of animals, most frequently mice.
Mouse models are leading to important discoveries relevant to pneumonia, but their limitations must be carefully considered. (i) pneumonia should be defined as an acute infection of the lung parenchyma by various pathogens, excluding the condition of bronchiolitis; The word pneumonia basically means inflammation of the lungs.
Older dairy calves are also vulnerable after housing in the autumn. What causes pneumonia in cattle? As the disease progresses, dyspnea, emaciation, and generalized weakness may become evident.
In medical parlance, pneumonia means inflammation in one or both lungs. Several approaches to establishing pneumonia in mice have been developed, and each has specific strengths and weaknesses. It is a multifactorial disease caused by a range of organisms including viruses, bacteria and mycoplasmas.
Calf pneumonia is a respiratory disease caused by inflammation in the lungs, primarily the alveoli (air sacs). Pneumonia is defined as inflammation of the lung parenchyma. The bacteria that cause pneumonia usually do so following on from the viral infections or when the air quality or husbandry is very poor.
Kennel Cough Infection in Dogs.

Goat Pneumonia Causes, Symptoms, Treatment Plan

NADIS National Animal Disease Information Service

Calf pneumonia from Vetlexicon Definitive Veterinary

Figure 1 from Acute or Atypical Interstitial Pneumonia
NADIS National Animal Disease Information Service

Wild boar lungs with and without macroscopic enzootic

Aspiration Pneumonia in Cats PetCoach
Aspiration Pneumonia in Pets Going Down the Wrong Pipe!
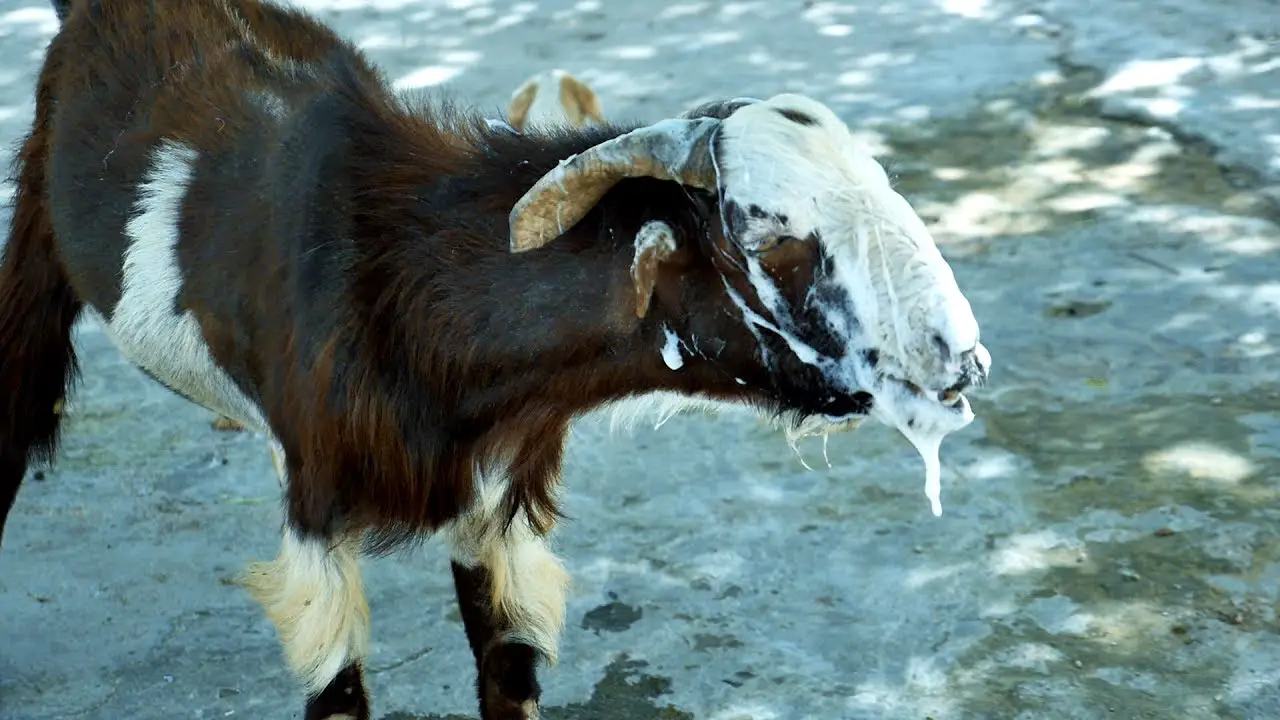

Pneumonia in Goats Complete Treatment Guide Boer Goat

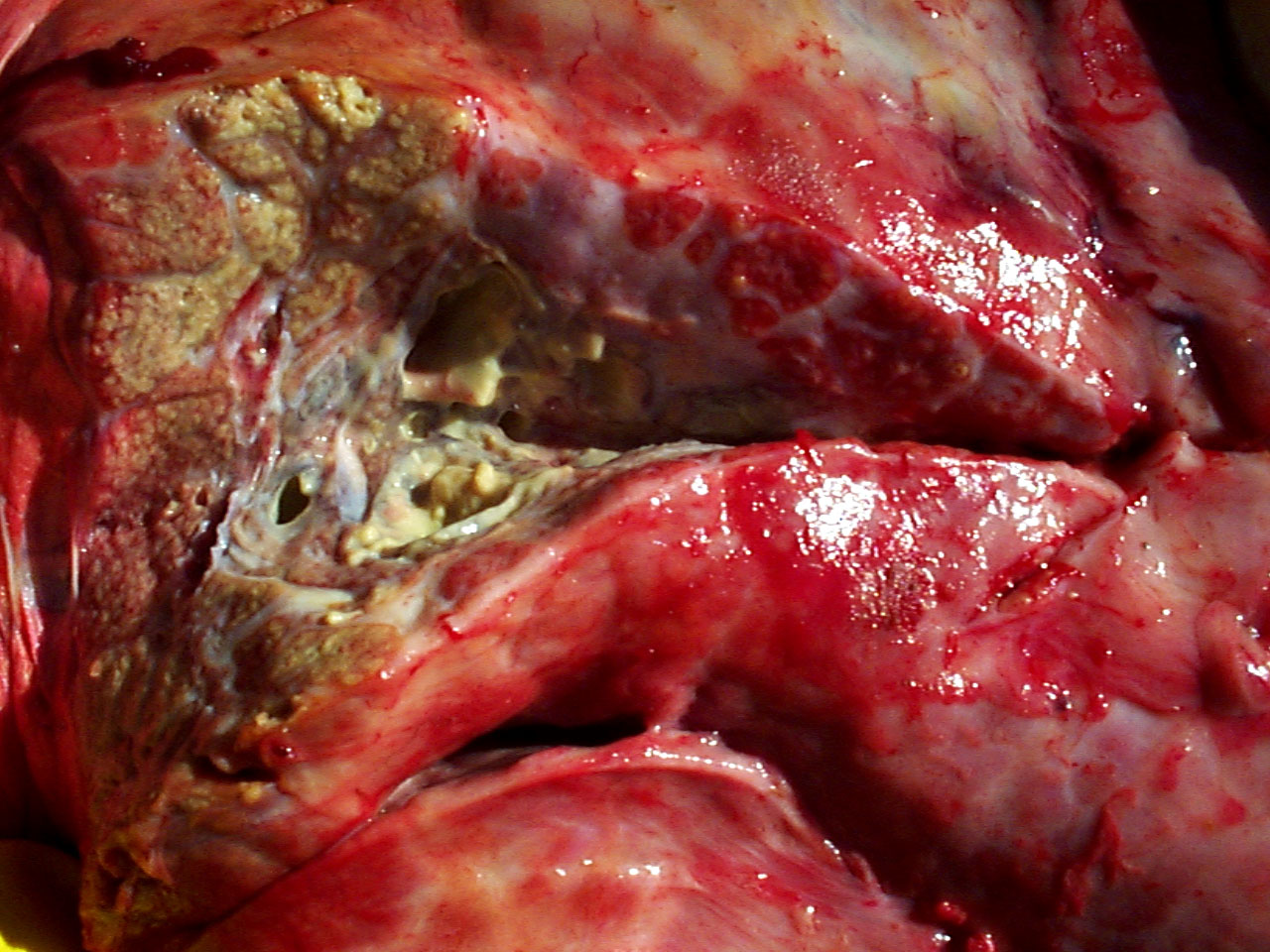
A) Lung showing fibrinous bronchopneumonia; the lung

Aspiration pneumonia from Vetlexicon Definitive

VetGrad 10 Minute Top Up Farm Animal 10 Min The
Pneumonia Management Mar Vista Animal Medical Center
PigProgress Pleuropneumonia (app)
Pneumonia Prevention is Better than Treatment Jay Harold
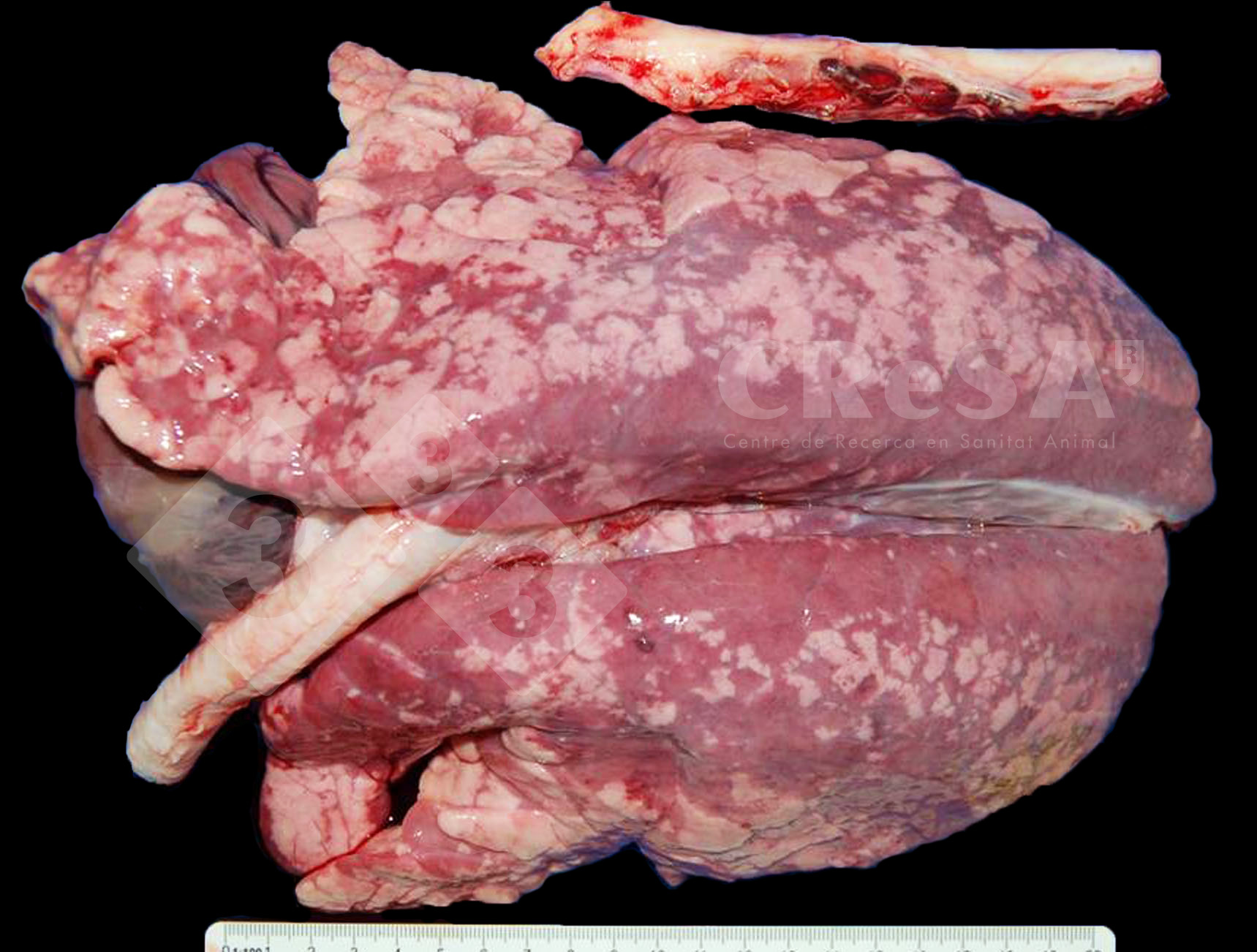
Interstitial pneumonia Atlas of swine pathology pig333
PigProgress Pleuropneumonia (app)

Severe, chronic, focally extensive necrotising pneumonia
Post a Comment for "Pneumonia In Animals"